Spatial Meshing Sample
The Spatial Meshing feature is marked as experimental because optimizations on the package and Snapdragon Spaces Service side are breaking backwards compatibility from release to release at the moment.
This sample demonstrates how to generate and visualize the spatial mesh approximating the environment in the real world.
For basic information about spatial meshing and what AR Foundation's AR Mesh Manager component does, please refer to the Unity documentation.
In order to use this feature it must be enabled in the OpenXR plugin settings located under Project Settings > XR Plug-in Management > OpenXR (> Android Tab).
How the sample works
ARMeshManager
The ARMeshManager component must be attached to a child of the ARSessionOrigin GameObject.
This component has a reference to the MeshFilter that will be generated when a mesh is available.
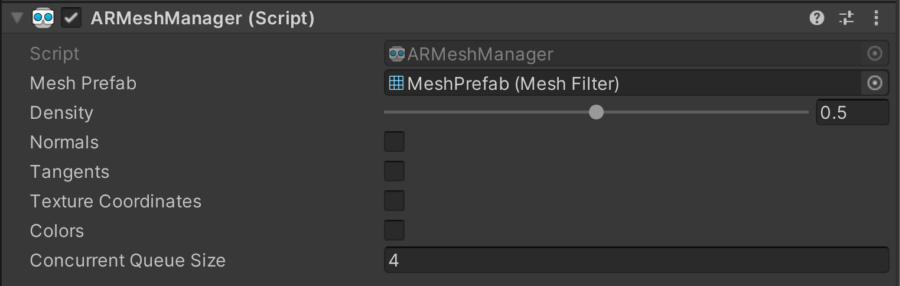
Attaching the ARMeshManager component to the camera object will result in changes to the object's Scale, from the original (1, 1, 1) to (10, 10, 10).
This will cause rendering issues of the application on headworn devices until the original camera scale is restored.
The following properties are unsupported:
- Changing the
Densityof the generated mesh is not currently supported. Tangents,Texture Coordinates, andColorsare not currently generated as part of the mesh. Accessing the buffers for these properties from theARMeshManagercomponent may generate null results.- Changing the
Concurrent Queue Sizeis not currently supported.
The Normals property is enabled by default.
Making a change to an unsupported ARMeshManager component property will be accompanied by a warning in the console when building the application.
By subscribing to the ARMeshManager component's meshesChanged callback, data can be retrieved about when a mesh is added, updated or removed.
Sample Code
private ARMeshManager _meshManager;
public void Awake() {
_meshManager = FindObjectOfType<ARMeshManager>();
}
public override void OnEnable() {
...
_meshManager.meshesChanged += OnMeshesChanged;
}
public override void OnDisable() {
...
_meshManager.meshesChanged -= OnMeshesChanged;
}
void OnMeshesChanged(ARMeshesChangedEventArgs args) {
foreach (MeshFilter meshFilter in args.added) {
...
}
foreach (MeshFilter meshFilter in args.updated) {
...
}
foreach (MeshFilter meshFilter in args.removed) {
...
}
}
Spaces AR Mesh Manger Config
The AR Mesh Manager component has properties that are not supported by the Snapdragon Spaces Unity package's subsystem implementation. Attempting to use any of the unsupported properties will display warnings when a build is run and the Spatial Meshing (Experimental) feature is enabled. It is recommended to use the (optional) Spaces AR Mesh Manager Config component, which has additional options to configure the generated mesh.
With this component, the Spatial Meshing provider can also handle a TrackingOriginMode.Floor related camera height offset coming from runtime side. The mesh could appear at a wrong position if this component is not used in that case.
This component must be attached to the same GameObject as the ARMeshManager component.
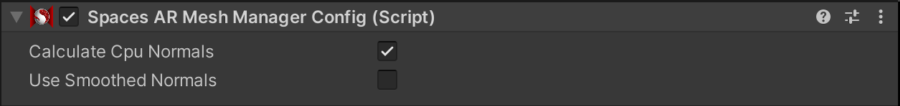
- Calculate CPU Normals:
- If enabled, cpu normals are calculated for each vertex in the mesh.
- Some vertices may be repeated in the mesh (using different indices).
- This can cause visible seams in the generated mesh.
- For every index in the mesh, each triangle referencing that index contribues to the resulting normal, but different indices (of repeated vertices) can have different normals.
- If the
Calculate CPU Normalsproperty and theNormalsproperty on theARMeshManagercomponent are not either both enabled or both disabled, an explanatory warning will be output in the console when building the application.
- Use Smoothed Normals:
- If enabled, cpu normals are smoothed for each vertex.
- All triangles referencing a vertex with the same space but a different index will treat those duplicate vertices as if they are the same vertex.
- This can cause hard edges in detected geometry to be less well defined, but reduces the appearance of seams.
- Calculating smoothed normals will use increased processing power, and have an impact on performance.
By default, when the sample is opened, it generates a mesh with its polygons adapted to the detected environment.
- When the
Calculate CPU Normalsproperty is enabled, the mesh is visualized with a Standard shader using theMesh With Cpu NormalsMaterial. - When the
Calculate CPU Normalsproperty is disabled, the mesh is visualized with the customMeshVisualization.shaderwhich generates normals for visualization purposes only.