Spatial Meshing Sample
This sample demonstrates how to generate and visualize the spatial mesh approximating the environment in the real world and how to use this mesh as a collider.
For basic information about custom trackable object updates and what Unreal Engine's AR Trackable Notify component does, please refer to the Unreal Engine documentation.
In order to use this feature, it has to be enabled in the plugin settings located under Project Settings > Snapdragon Spaces plugin.
How the sample works
By default, when the sample is opened, it generates geometry with its polygons adapted for the detected environment. The user can also change the opacity of the spatial mesh using the slider of the UI, hide or show the mesh, choose between CPU or GPU computed normals, generate the colliders (which will stop the mesh updates) and spawn a ball to show the colliders physics interaction.

Spatial Meshing AR Manager
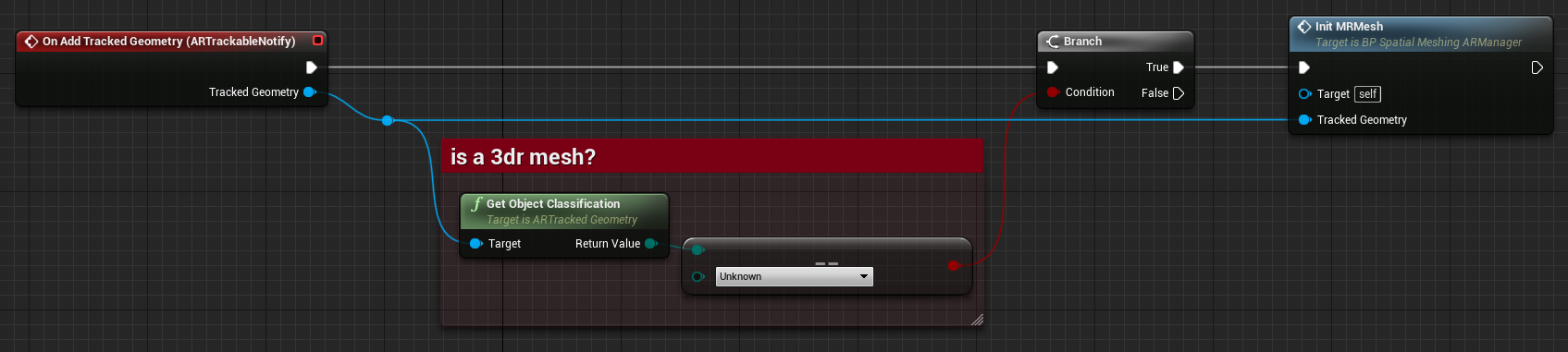
The BP_SpacesARManager_SpatialMeshing blueprint file (located under SnapdragonSpacesSamples Content > SnapdragonSpaces > Samples > Spatial Meshing > Placeable) centralizes the actions of creating and destroying meshes as augmented geometries through an event system.
This blueprint binds events from the AR Trackable Notify component to react to AR trackable geometries changes. When the system is not using the normals to detect geometries, it invokes the On Add/Update/Remove Tracked Geometry events. The different types of objects reported by the AR Trackable Notify component can be registered as UARTrackedGeometry, to verify that the tracked geometry is a spatial mesh, its object classification must be EARObjectClassification::Unknown. The GetObjectClassification function can be used to check the classification. In Spatial Meshing, only EARObjectClassification::Unknown is supported, meaning that object classification is currently not supported.
The Render Spatial Mesh node returns an actor containing the detected geometry with applied normals. Unreal Engine displays the parameters by reference as return values and for this reason, it is mandatory to pass the reference of the actor that represents the geometry and the variable representing the number of the previous indices as well. Otherwise, multiple actors will be created multiple times over. The On Spatial Mesh Normals Computed delegate can be listened to, to avoid unnecessary calls, and update the visualization of the mesh (using the Render Spatial Mesh node) only if the calculation for the normals is completed. This calculation is done in an asynchronous thread for better performance and calls the delegate when finished.
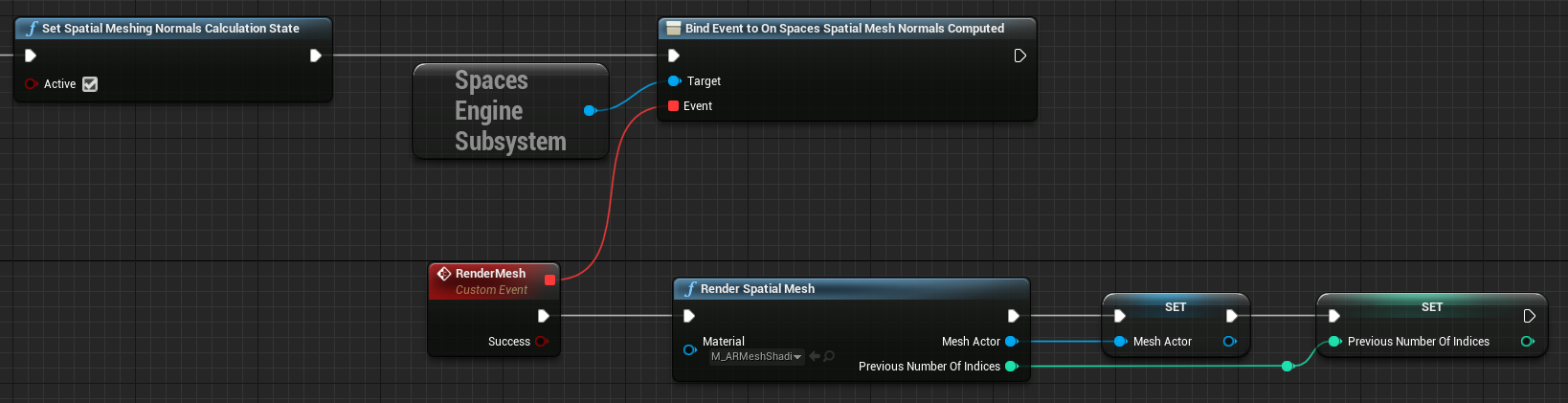
The Set Spatial Meshing Normals Calculation State node is useful to enable or disable the normals calculation from CPU. Furthermore, the Get Spatial Meshing Normals Calculation Statereturns true, if the normals calculation is enabled.
In the sample blueprint, to start detection, set Toggle AR Capture to ON. To stop detection, set it to OFF. Stopping detection will destroy all generated AR geometry. Additionally, Scene Understanding must be set as the capture type of that node.
Spatial Meshing AR Session Config
The system starts using the D_SpacesSessionConfig_SpatialMeshing asset (located under SnapdragonSpacesSamples Content > SnapdragonSpaces > Samples > Spatial Meshing > Core) to detect the geometries. This asset is a data asset derived from the SpacesSessionConfig class.
The session config file provides a field to add bounds. Each bound represents a volume, and geometries entirely outside this volume are not displayed. The number of bounds must be greater than zero to track the meshes.