Virtual Force Feedback (VFF)
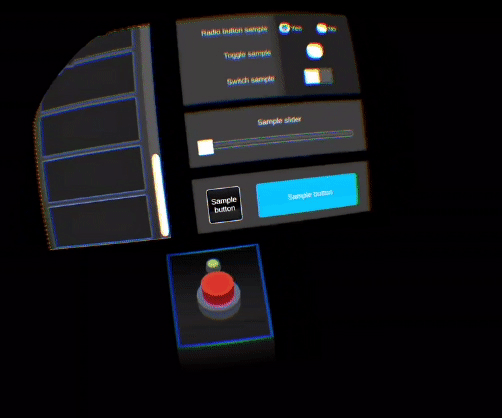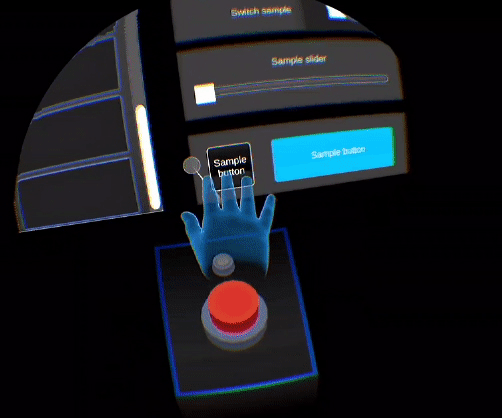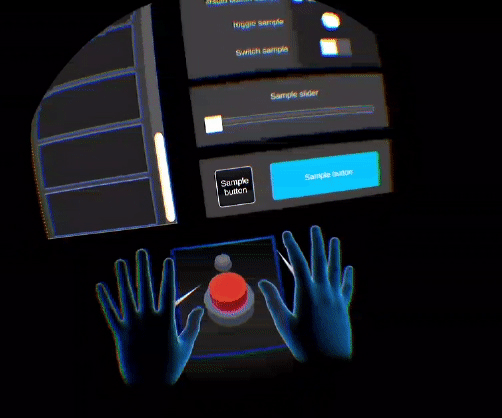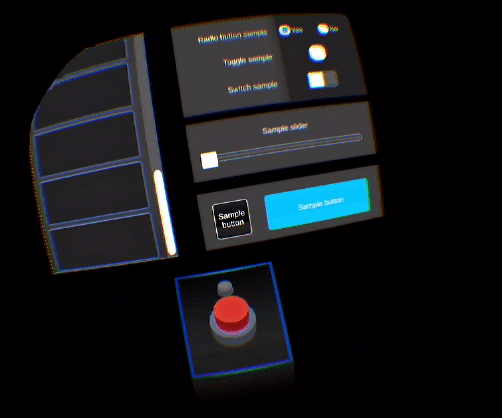
This feature gives the user the feeling to interact with a solid virtual object: it helps to overcome the lack of haptic feedback. When interacting with a virtual object, the hand avatar will split into two hand representations. The ghost hand (from user's hand behavior) will continue its movement while the main one will stay stuck on the virtual element (constrained by physics).
Main hand
The hand avatar in the VFF context also represents the behavior of the user's real hand, but the hand stays against an object with which there is a collider to create the feeling of a virtual haptic feedback.
Ghost hand

The purpose of the ghost hand is to represent the real-time behavior of the user’s hand. It appears when the hand avatar collides with an object. Its appearance is made gradually and discreetly so as not to disturb the user.
VFF Setup
To enable the VFF feature, Hand Model prefabs need to be changed on the XR Hand Tracking Manager component. Predefined VFF compatible models, QualcommHandLeftVFF and QualcommHandRightVFF, can be found under QCHT Unity Interactions > Prefabs > Hands > Resources. Those models use Hand Physics Part, Rigid Body and Configurable Joint components to enable the Virtual Force Feedback feature.
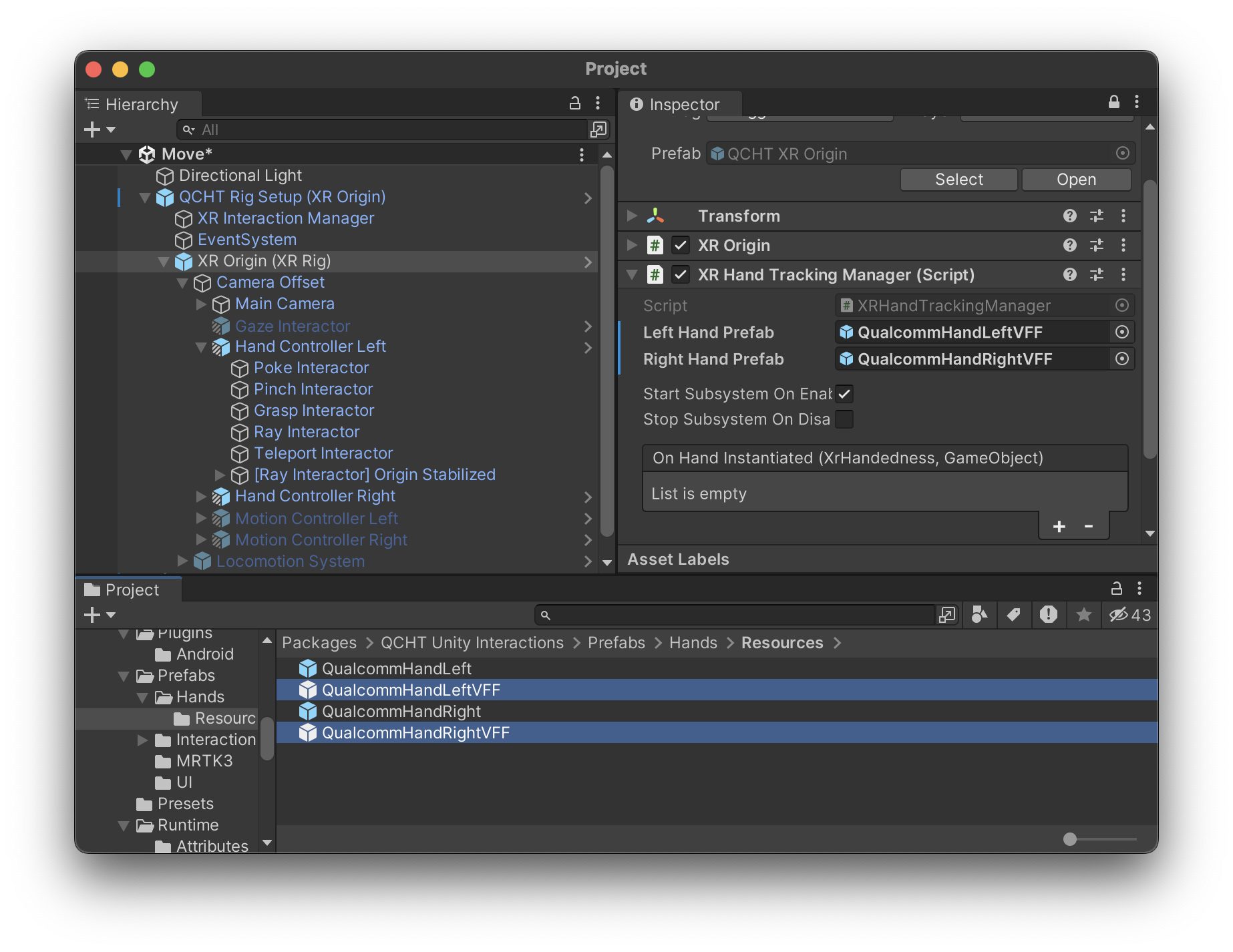
Once instantiated, the VFF feature can be toggled on demand using bool TrySetVff(XrHandedness handedness, bool active) on XR Hand Tracking Manager API. This function will seek for IHandPhysible interface on model instance to perform VFF toggling.
This feature is considered as visualisation feedback only, meaning that interactors poses, like Proximal Interactors won't be affected by the physical context. Those will continue to rely on the true hand position (the ghost hand) when the main hand collides a physical object.